Ultrasound-Guided Stellate Ganglion Blocks
Ultrasound-Guided Stellate Ganglion Blocks
Related Topics:
Stellate Ganglion Blocks: A Promising Treatment for CRPS and PTSD
Stellate ganglion blocks (SGBs) are gaining recognition as a powerful tool in treating several complex medical conditions. Most notably, they have shown significant promise in addressing complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Furthermore, when guided by ultrasound, the procedure becomes even safer and more precise.
What Are Stellate Ganglion Blocks?
Stellate ganglion blocks are injections that target nerves in the neck called the stellate ganglion. These nerves are part of the sympathetic nervous system, which influences pain perception and the body’s stress response.
By delivering a local anesthetic to this nerve cluster, SGBs temporarily block sympathetic nerve activity. As a result, this helps alleviate pain, improve blood flow, and modulate stress-related neurocircuitry in the brain.
In addition, the calming effect on the sympathetic nervous system may improve symptoms in both pain and trauma-related conditions.
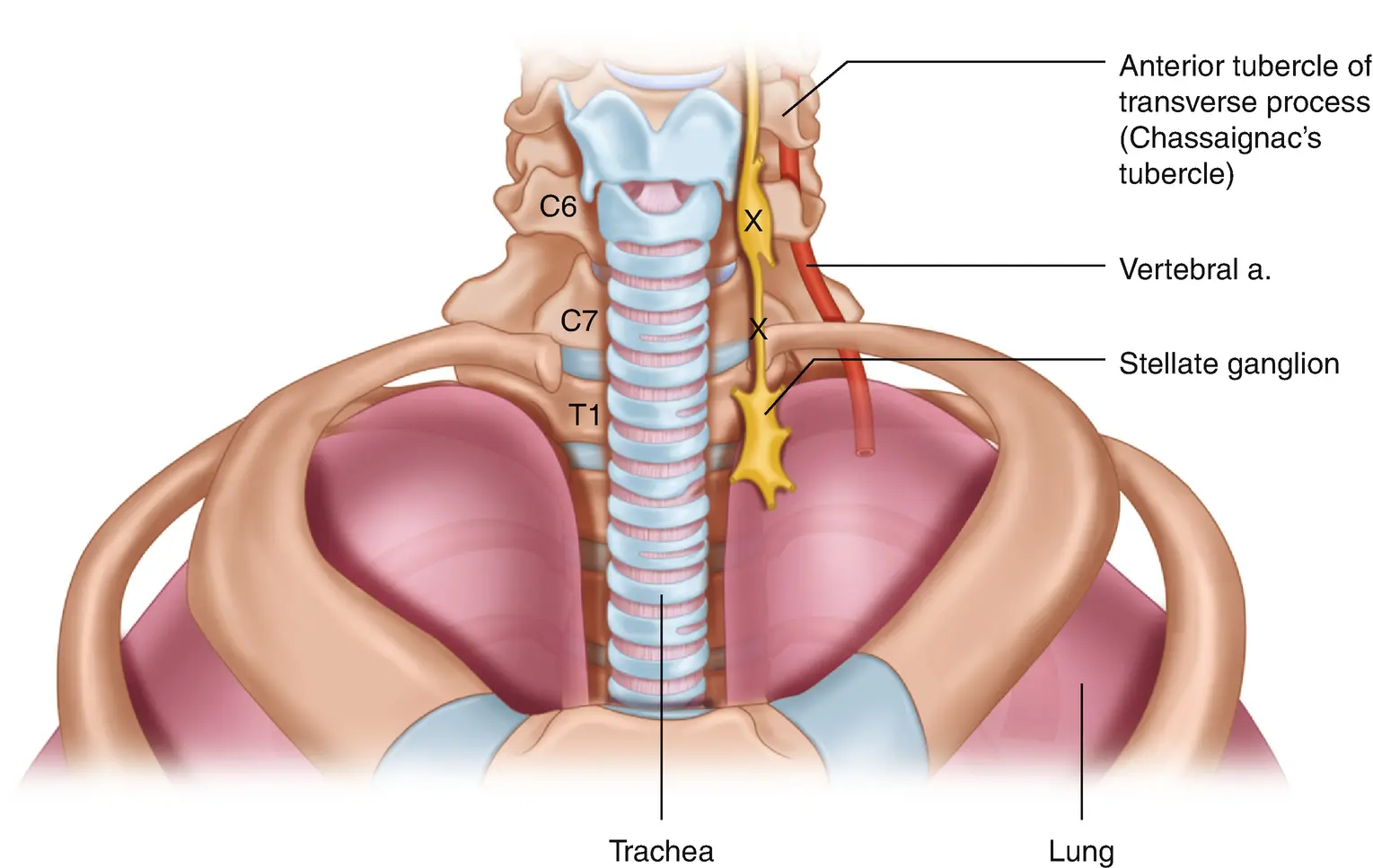
How SGBs Work in the Body
The stellate ganglion is a collection of nerves that influence blood flow, pain perception, and the fight-or-flight response. In PTSD, this nerve cluster is believed to affect key brain structures like the amygdala, which plays a central role in processing fear and emotional memory. By modulating activity in these circuits, SGB may help reduce the intensity and frequency of trauma-related symptoms.
In CRPS, abnormal sympathetic signaling causes exaggerated pain responses, swelling, and color changes in the affected limb. Therefore, stellate ganglion blocks disrupt this cycle by quieting the sympathetic nerves and resetting the overactive responses. For many patients, this break in the cycle brings noticeable relief.
Consequently, the procedure has gained traction as part of comprehensive pain and psychiatric treatment programs.
SGBs for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
CRPS is a notoriously difficult condition characterized by chronic, severe pain often following trauma or surgery. According to the American Academy of Pain Medicine guidelines, sympathetic nerve blocks like SGBs are recommended for CRPS, especially when the pain is sympathetically maintained.
Recent meta-analyses and clinical guidelines support the use of stellate ganglion blocks as part of a multimodal treatment strategy, often in combination with medications, physical therapy, occupational therapy, or psychological support. For example, a systematic review in Pain Physician (2024) confirmed that SGB therapy significantly reduces pain intensity in CRPS patients, with minimal adverse events reported.
In a retrospective study of over 800 ultrasound-guided SGBs performed for CRPS and other neuropathic conditions, most patients experienced meaningful reductions in pain. Additionally, the data suggest that repeat blocks, sometimes in a series of two or more, can further increase benefit.
As such, SGBs represent an important component of the CRPS treatment algorithm.
Stellate Ganglion Blocks for PTSD
Emerging research has highlighted SGBs as an effective option for PTSD. A randomized clinical trial published in JAMA Psychiatry found that patients receiving SGB treatment experienced significantly greater reductions in PTSD symptom severity than those receiving sham treatments.
SGBs appear particularly useful in reducing hypervigilance, anxiety, and re-experiencing symptoms. While the exact mechanism is still under investigation, imaging studies suggest SGB may modulate amygdala hyperactivity—the brain region associated with fear and trauma responses.
Moreover, behavioral health clinicians increasingly recommend SGBs as a useful adjunct to trauma-focused therapy. These blocks appear especially effective for treatment-resistant PTSD, where traditional medications and psychotherapy may fall short.
In summary, SGB offers a promising neurobiological tool to complement psychological treatment.
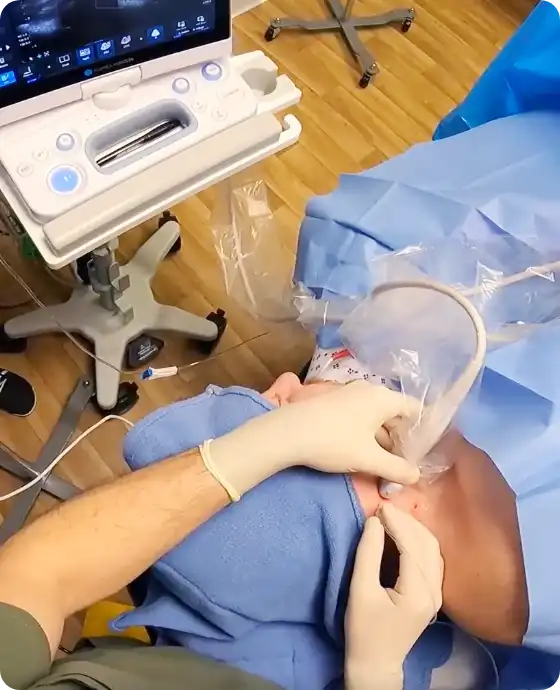
Why Ultrasound Guidance Matters
Ultrasound guidance offers real-time visualization of anatomical structures during the procedure, dramatically improving precision and safety.
Key advantages include:
-
Reduced risk of vascular injury
-
Increased accuracy of anesthetic placement
-
Lower incidence of complications
-
No radiation exposure compared to fluoroscopy
Studies show ultrasound-guided SGBs are at least as effective as fluoroscopy-guided techniques, if not superior. A cadaveric study published in Pain Medicine (2021) confirmed ultrasound guidance offered comparable, if not improved, accuracy with reduced risk.
Therefore, ultrasound guidance should be the standard of care for this procedure.
Common Side Effects and Complications
While generally well-tolerated, SGBs do carry some risks:
Common side effects include:
-
Hoarseness (3.9%)
-
Difficulty swallowing (3.4%)
-
Temporary Horner’s syndrome (ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis)
-
Mild dizziness or flushing
Rare but serious complications include:
-
Vascular injury
-
Hematoma
-
Pneumothorax
-
Intravascular injection leading to seizures or neurologic events
Fortunately, ultrasound guidance greatly reduces these risks. The overall complication rate when using ultrasound is very low, making this a safe procedure when performed by experienced providers.
As always, proper patient selection and technique are critical to minimizing risks.
Conditions Beyond CRPS and PTSD
Stellate ganglion blocks may also help with:
-
Phantom limb pain – Small case series and early clinical reports suggest benefit, though larger trials are needed
-
Refractory angina
-
Hot flashes and vasomotor instability (especially in breast cancer survivors)
-
Migraines and facial pain
Research in these areas is ongoing. Nevertheless, early studies show promise.
For this reason, SGB is being explored across a broad spectrum of sympathetically mediated conditions.
How Often Are Stellate Ganglion Blocks Performed?
Once considered a niche technique, SGBs are now increasingly common in pain and behavioral health practices. Patients often undergo one to three blocks to determine effectiveness. In some cases, maintenance blocks are scheduled if benefits wane over time.
Importantly, patients with CRPS or PTSD often report relief within 30 minutes to 24 hours of treatment. When successful, many describe it as a “reset” for their nervous system.
Accordingly, the use of SGB is expanding as awareness and access improve.
Who Is a Good Candidate for SGB?
You may benefit from stellate ganglion blocks if you have:
-
CRPS of the upper limb
-
PTSD not fully responding to therapy or medication
-
Severe sympathetic pain disorders
-
Refractory neuropathic pain
Your provider will evaluate your medical history, current symptoms, and response to prior therapies before recommending the procedure.
Thus, individualized evaluation is essential for optimal outcomes.
What to Expect During the Procedure
Key Expectations for Patients
Procedure Time: 10–20 minutes
Recovery: Most patients return to normal activities the next day. Temporary side effects like voice changes or eyelid droop may occur.
Monitoring: Patients are observed for 30–60 minutes after the procedure.
Adjunct Care: We often pair the procedure with physical therapy for CRPS or psychotherapy for PTSD to support long-term results.
SGBs are outpatient procedures performed with care and precision. We begin by cleaning the skin to reduce the risk of infection and conducting a time-out procedure for safety. After anesthetizing the skin with lidocaine, we use ultrasound to visualize the neck anatomy in real time. The needle is carefully advanced under ultrasound guidance, and the local anesthetic is injected around the stellate ganglion.
Afterward, patients are monitored and typically return to daily activities the following day. In addition, we often coordinate follow-up care with physical therapists for CRPS or mental health providers for PTSD to enhance outcomes.
Together, these steps help ensure safety, efficacy, and continuity of care.
Conclusion
Stellate ganglion blocks are an effective and well-tolerated treatment for CRPS and PTSD. With ultrasound guidance, the procedure becomes even safer and more precise.
If you’re struggling with unresolved nerve pain or trauma symptoms, Red Butte Pain Solutions can help. We offer advanced diagnostic tools and treatment options—including ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion blocks—to help you feel like yourself again.
Schedule now or call us at 602-633-4334 to explore whether SGB is right for you.
Phantom Limb Pain: One Bad Opera
Phantom limb pain affects people who have lost a limb due to injury, surgery, or a birth defect. This pain is real, not imagined, and occurs because the brain and nervous system still register signals from the missing limb. If you or a loved one is struggling with...
Do Stims Stim? 20-Years of Spinal Cord Stimulation Innovation
Over the last 20 years, spinal cord stimulation has transformed significantly. It’s evolved from a basic pain relief option to a sophisticated, adaptable therapy with specialized features. When spinal cord stimulators (SCS) first emerged, they offered hope but little...
Breaking New Ground in Pain Management: DTM and Closed-Loop Spinal Cord Stimulation
When I was in training, I was taught that "Stims stim," meaning there wasn’t much difference between spinal cord stimulation (SCS) devices beyond customer service for our patients. Back then, no SCS devices had MRI compatibility, and the only real debate was whether...
Overcoming Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Resilience and Recovery
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) is a perplexing and often debilitating condition. It can turn a minor injury into a chronic...
