Welcome back to our spinal cord stimulator series, “Do Stims Stim?” If you’ve been with us through our exploration of HFX , DTM, and closed-loop stimulation, you’re in for another intriguing journey. Today, we’re diving into the world of Burst stimulation. We’ll explore how Burst stimulation works, compare it to other models like DTM and HFX, and examine the evidence supporting its efficacy.
Understanding Burst Stimulation
Burst stimulation is a unique form of spinal cord stimulation (SCS). It mimics the natural firing patterns of neurons. Traditional SCS delivers a constant electrical pulse. In contrast, Burst stimulation delivers groups, or “bursts,” of pulses. These bursts aim to more closely replicate the body’s natural nerve signaling.
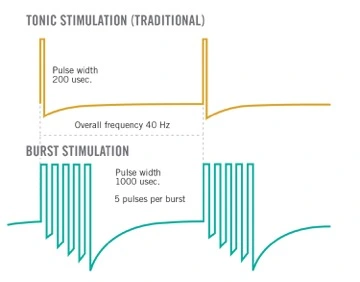
This mode of stimulation was developed to address the limitations of traditional paresthesia-based SCS. Many patients report a tingling sensation with traditional SCS. Burst stimulation, however, can provide pain relief without this sensation. This is particularly beneficial for patients who find the tingling uncomfortable or distracting.
How Burst Stimulation Works
Burst stimulation operates by delivering electrical pulses in rapid sequences. These sequences mimic the natural firing patterns of the brain. Each burst consists of five pulses delivered at 500 Hz. This pattern is followed by a brief pause. This approach allows for modulation of the pain pathway at a higher level.
The mechanism behind Burst stimulation involves both the spinal cord and the brain. It targets the dorsal column of the spinal cord, similar to traditional SCS. However, it also engages the brain’s pain processing pathways. This dual action can enhance pain relief and improve patient outcomes.
Comparing Burst, DTM, and HFX Stimulation
Now, how does Burst stimulation compare to DTM and HFX? Each of these has its unique approach and benefits.
DTM Stimulation focuses on targeting both neurons and glial cells. It uses a varying frequency to modulate pain pathways. DTM aims to address the complex interplay between different cell types in the spinal cord. This broader approach can enhance pain relief for some patients.
HFX Stimulation offers high-frequency, paresthesia-free stimulation. It operates at a frequency of 10 kHz, providing pain relief without the tingling sensation. HFX is particularly beneficial for patients who prefer a non-perceptible form of stimulation.
Burst Stimulation, on the other hand, focuses on mimicking natural neuronal firing. It provides pain relief without causing a paresthesia sensation. Burst can be particularly effective for patients who have not found relief with other SCS types.
Efficacy of Burst Stimulation
The efficacy of Burst stimulation is supported by several studies. Research shows it can provide significant pain relief for chronic pain patients. In some cases, it has outperformed traditional paresthesia-based SCS.
One key study demonstrated Burst stimulation’s ability to reduce pain scores significantly. Patients reported greater satisfaction and improved quality of life. The study highlighted Burst’s potential in treating various chronic pain conditions.
Another study compared Burst stimulation directly with traditional SCS. Results showed that Burst provided superior pain relief for many participants. Additionally, patients experienced fewer side effects, such as paresthesia.
Advantages of Burst Stimulation
Burst stimulation offers several advantages over traditional SCS models. First, it can provide pain relief without paresthesia. This is a significant benefit for patients sensitive to tingling sensations. Burst’s ability to mimic natural neuronal firing can also enhance its efficacy.
Patients often report improved mood and quality of life with Burst stimulation. This is likely due to its effect on the brain’s pain processing pathways. By engaging both the spinal cord and the brain, Burst can offer a more comprehensive approach to pain management.
Considerations and Challenges
Despite its benefits, Burst stimulation is not suitable for everyone. Some patients may not respond to this type of stimulation. It’s important for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers. Together, they can determine the most appropriate treatment for their specific needs.
Implanting a spinal cord stimulator involves surgery. As with any surgery, there are risks involved. Patients should discuss these risks with their healthcare provider. Understanding the potential risks and benefits is crucial for making an informed decision.
Future of Spinal Cord Stimulators
The future of spinal cord stimulators is promising. Innovations like Burst, DTM, and HFX are expanding treatment options. These advancements are helping more patients find relief from chronic pain.
Researchers continue to explore new ways to improve SCS technology. The goal is to enhance efficacy, reduce side effects, and improve patient outcomes. As technology advances, we can expect even more exciting developments in the field.
Conclusion
Burst stimulation represents an exciting advancement in spinal cord stimulator technology. Its ability to mimic natural neuronal firing offers a unique approach to pain management. For many patients, Burst provides significant pain relief without the feeling of paresthesia.
As we’ve seen, Burst, DTM, and HFX each have their strengths. The choice of stimulation depends on the individual patient’s needs and preferences. It’s important for patients to discuss their options with their healthcare provider.
We hope this exploration of Burst stimulation has been informative. If you have any questions or would like to learn more, feel free to reach out. Stay tuned for more insights into the world of spinal cord stimulators in our ongoing series
